nexus ct head
Deficits in short-term memory. NEXUS Chest is a clinical decision rule that supports the appropriate use of thoracic imaging in trauma.

Schematic Overview Of The Most Common Types Of Craniosynostosis Download Scientific Diagram
He is best known for the development of the Ottawa Ankle Rule the Canadian C-Spine Rule and Canadian CT Head Rule and as the Principal Investigator for the landmark OPALS Studies for prehospital care.
. Performance of a decision rule to predict need for computed tomography among children with blunt head trauma. Make sure to check out The ED Guide to Neuroimaging. Pan-scan CT scan from head through pelvis is used routinely in many trauma centers in spite of the American College of Surgeons inclusion of avoidance of routine whole body CT in trauma in its Choosing Wisely recommendations.
BackgroundClinicians afraid of missing intracranial injuries liberally obtain computed tomographic CT head imaging in blunt trauma patients. Physical evidence of trauma above. The sensitivity of NEXUS II rule was 9375 specificity was 394.
Sharp MD MS American College of Emergency. Drug or alcohol intoxication. We set out to externally validate this CDR in a large cohort.
The NEXUS criteria may not be reliable with patient 65 years of age however 4. Canadian CT Head Rule. Oman JA Cooper RJ Holmes JF et al.
The NEXUS Head CT decision instrument was developed as a one way instrument which would hopefully serve to rule out those children who might otherwise receive imaging as opposed to classifying many as high risk In the original cohort use of NEXUS Head CT decision instrument decreased the need for CT by 25. CT ordering was per physician discretion. Read about the uses procedure and risks of CT head scans here.
If you or your business has a connection nexus with Connecticut you may owe Connecticut tax. The Canadian Head CT Rule Canadian New Orleans Criteria New Orleans NEXUS II Head CT Rule NEXUS and PECARN. Head CT after Trauma.
Objective The National Emergency X-Radiography Utilisation Study II NEXUS II clinical decision rule CDR can be used to optimise the use of CT in children with head trauma. Part two of this series examines the literature regarding the appropriate use of the head CT in blunt head trauma a common clinical grey zone in emergency medicine. New Orleans Head CT Rule.
We performed a prospective observational study of patients aged head trauma of any severity to 10. 6 19 In the original cohort of all ages the NEXUS Head CT DI exhibited 100 sensitivity for patients requiring an intervention and 99 sensitivity for patients who had an injury evident. Melnick MD MHS Adam L.
We set out to externally validate this CDR in a large cohort. Although prior studies have demonstrated increased identification. This decision instrument was only to be used for children in whom imaging was being considered a judgment first decision instrument next approach.
There are seven criteria 12. The NEXUS criteria have a sensitivity of 996 for ruling out cervical spine injury in the original study validating the criteria 95 confidence interval 986-100 2. Prior work suggests that clinical criteria NEXUS Head CT decision instrument can reliably identify patients with important injuries while excluding injury and the need for imaging in many patientsMethodsWe conducted a.
CT use in the evaluation of trauma patients has risen dramatically in recent years. Nexus means a connection or a link. The Canadian CT Head Rule for patients with minor head injury.
In about 1000 children these criteria were 100 sensitive 33 specific for neurosurgical intervention but the 95 CI was wide 87-100. An individual with nexus may be required to pay. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
In a study of over 9500 patients aged over 14 years the absence of the above criteria was used to rule out thoracic injury with a negative predictive value of 985 and exclusion of clinically major injury. Check each tax type below for its nexus standard. The NEXUS Criteria for C-spine Imaging clears patients from cervical spine fracture clinically without imaging.
Mower WR Hoffman JR Herbert M et al. Stiell is the Principal Investigator for 1 of 3 Canadian sites in the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium ROC which is funded by CIHR NIH HSFC AHA and. No midline spinal tenderness.
A noncontrast head CT indicate in head trauma patients with LOC or post-traumatic amnesia only if 1 of following is present. A computed tomography CT scan of the head creates images of the skull brain and other parts of the head. 8 United States level 1 trauma centers enrolled patients for derivation and validation of a decision instrument to aid in the decision to perform a chest CT in patients with blunt trauma.
As compared with the NEXUS Low-Risk Criteria. Methods We performed a prospective observational study of patients aged head trauma of any severity to 10. A business with nexus is required to register with DRS and pay or collect from its customers Connecticut taxes.
Wells GA Vandemheen K et al. How to improve care and decrease imaging for adults Edward Ted R. Developing a decision instrument to guide computed tomographic imaging of blunt head injury patients.
The National Emergency X-Radiography Utilisation Study II NEXUS II clinical decision rule CDR can be used to optimise the use of CT in children with head trauma. 1 NEXUS II 20023 Age 65yr Recurrent or forceful vomiting Evidence of significant skull fracture Scalp hematoma Neurologic deficit Altered Alertness GCS 15 Abnormal behavior. Our study was undertaken with that goal in mindto assess the performance of a previously derived and validated DI the NEXUS Head CT DI as it applies to patients under 18 years old.
PDF The imaging method of choice to precisely diagnose intracranial injuries is a head CT scan. You might be interested in. 1 The rule has two sub-rules one for detection of major injuries and one for detection of all injuries major and minor injuries in hemodynamically stable non-intubated patients.

Neck Trauma Diagnosis And Management In The Emergency Department Trauma Extra Supplement Trauma Cme Digest

Diagnostic Accuracy And Failure Mode Analysis Of A Deep Learning Algorithm For The Detection Of Intracranial Hemorrhage Journal Of The American College Of Radiology
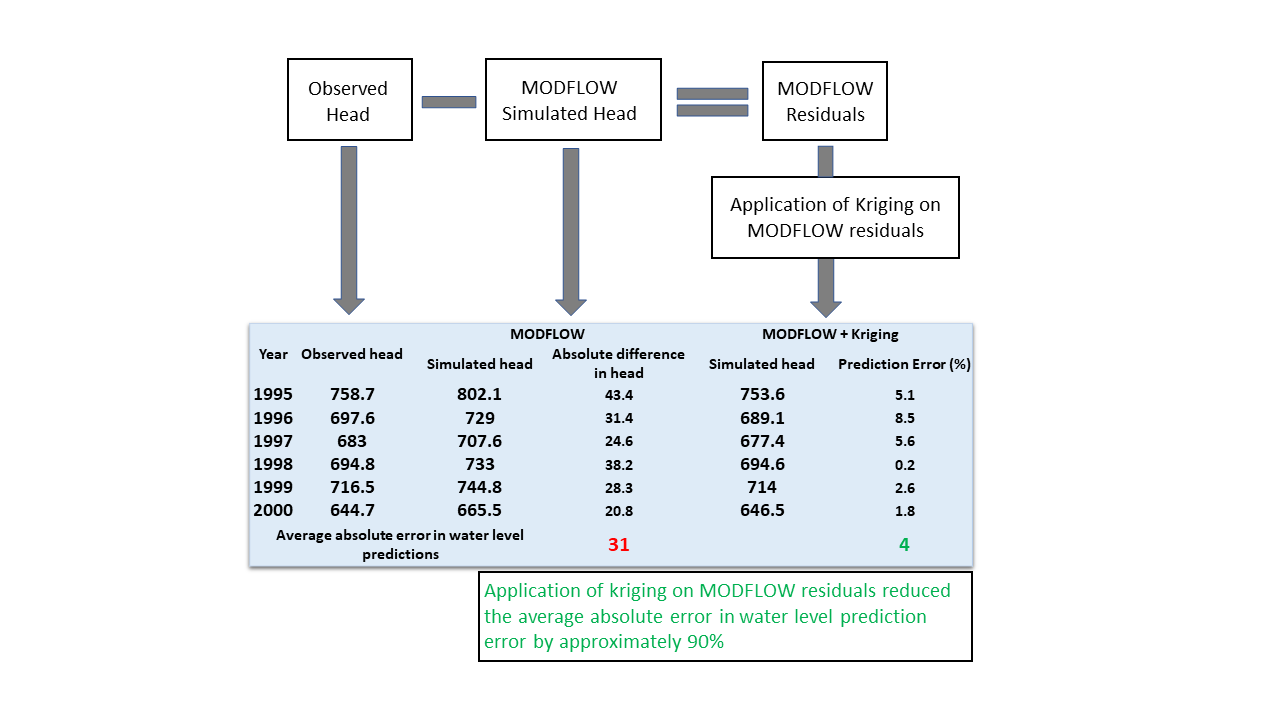
Water Free Full Text Minimizing Errors In The Prediction Of Water Levels Using Kriging Technique In Residuals Of The Groundwater Model Html
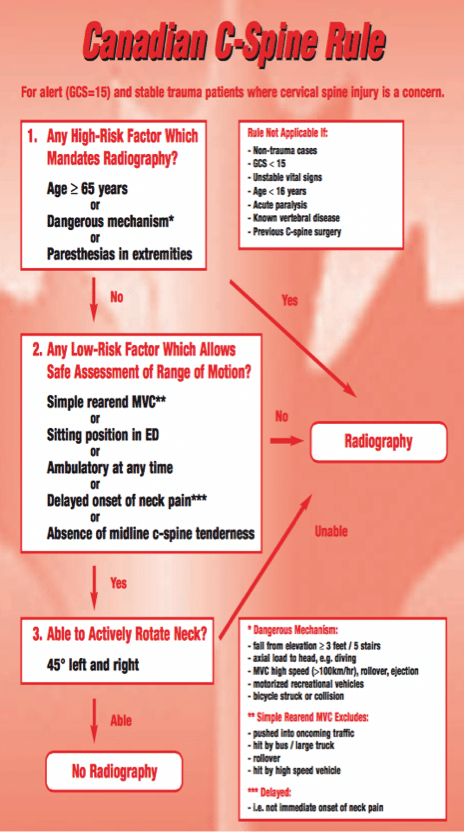
Back And Neck Injuries Emergency Care Institute
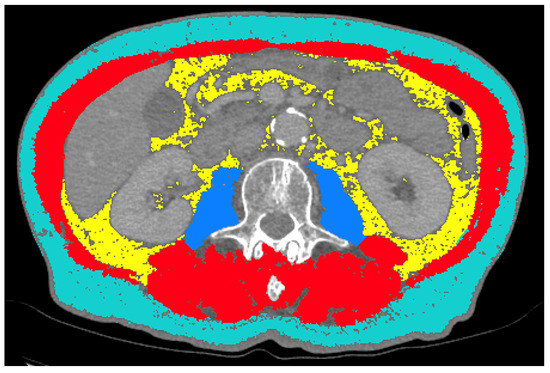
Cancers Free Full Text Ct Body Composition Of Sarcopenia And Sarcopenic Obesity Predictors Of Postoperative Complications And Survival In Patients With Locally Advanced Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Html

Mild Head Injury Archives Emergency Medicine Kenya Foundation

Ppt Approach To Trauma Patients Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3662502

Figure 14 From Head Computed Tomography Interpretation In Trauma A Primer Semantic Scholar

Can The Important Brain Injury Criteria Predict Neurosurgical Intervention In Mild Traumatic Brain Injury A Validation Study The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Figure 14 From Head Computed Tomography Interpretation In Trauma A Primer Semantic Scholar

Head Injury In Pediatric Patients To Ct Or Not To Ct

Diagnostic Accuracy And Failure Mode Analysis Of A Deep Learning Algorithm For The Detection Of Intracranial Hemorrhage Journal Of The American College Of Radiology

The Sgem Paper In A Pic The Skeptics Guide To Emergency Medicine

Axial Slice Of A Non Contrast Ct Head At The Level Of The Basal Ganglia The Basal Ganglia Are A Group Radiology Radiology Imaging Diagnostic Imaging

Figure 14 From Head Computed Tomography Interpretation In Trauma A Primer Semantic Scholar


Comments
Post a Comment